Oracle
Oracle Database is an enterprise relational database. It can run transaction processing, data warehousing, and multi-model database workloads such as machine learning, spatial, and graph analysis. Recent versions of Oracle Database also added support for JSON and blockchain use cases, and the software can be run in on-premise, cloud or hybrid environments.

How does Oracle fit with Python?
The Python community and Oracle have a long history. The excellent Python Database API-compliant "cx_Oracle" interface for Oracle Database was first created by the user community in 1998 and is now being enhanced and maintained by Oracle. The cx_Oracle module also underpins the Oracle Machine Learning for Python engine. Oracle's high-performance GraalVM framework supports an implementation of Python called GraalPython.
Why is Oracle Database a great choice?
Oracle Database is cross-platform, supporting multiple hardware platforms and various operating systems. Developers and companies of all sizes rely on its proven industry-leading performance, scalability, reliability, and security. As data volumes rise exponentially, new data types and data models are required to support modern applications. Oracle Database supports the following data types at no extra cost:
- JSON
- Blockchain
- XML
- Object
- Graph
- Spatial
- Time Series
- Relational
With support for scale-out database clusters, sharded distributed systems, and disaster recovery with continuous application availability, there is no shortage of features to guarantee the Database continues to run uninterrupted 24/7.
Oracle makes its enterprise-class database readily available to developers with its free on-premises edition Oracle Database XE or on the Oracle public cloud with an Always Free Cloud account. In addition, Oracle Autonomous Database is a popular choice for developers as no database management or tuning is required, leaving developers to do what they do best – writing code for their applications.
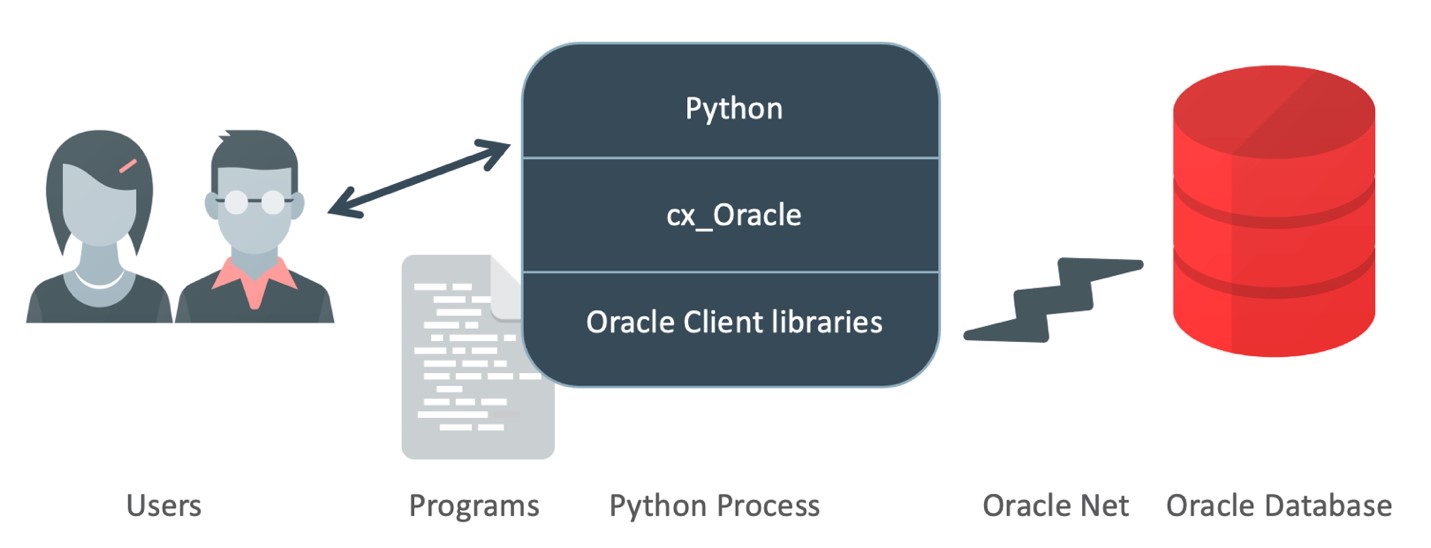
Connecting to Oracle Database with Python
As with any database, applications require a connector or driver to connect to the Oracle Database. The Python DB API-compliant cx_Oracle interface provides developers access to standard and advanced Oracle Database features, such as SQL execution and document storage APIs. It also gives users access to network traffic encryption capabilities and Oracle's leading high availability features.
Code examples and free workshops such as the introductory Python and Oracle for Developers Workshop and a full-stack development workshop using Python with SQLAlchemy to Oracle Database are available.
You can use many Python frameworks and object-relational mappers (ORMs) with Oracle Database. ORMs abstract the tables and objects in a relational database to objects that Python developers can manipulate and operate on. SQLAlchemy and Django are popular ORMs. SQLAlchemy is used by Pandas, which is very popular with Oracle users. The table below shows the relationship between web framework, ORM, driver, and the Oracle Database.

Learn more about Python ORMs on that dedicated topic page.
ORMs provide a familiar programming model for Python developers, but sometimes you want that extra performance and operate closer to SQL objects. Oracle cx_Oracle offers several functions to deliver that performance. These functions include fetching data, binding data, executing PL/SQL, operating on LOBs, JSON documents, message passing with Oracle Advanced Queuing, and more.
Oracle and Data Safety
According to Gartner, Oracle has one of the highest data safety ratings in the industry, with a wide range of features for data protection and high availability. These features include:
-
Access control to rows in a table
-
Database vault to restrict privileges and access
-
All in one data security service in the Oracle Cloud with Data Safe
-
Oracle also provides free tools such as the Database Assessment Tool (DBSAT) to help you identify and remedy potential vulnerabilities.
Oracle also provides numerous data recovery features, including:
-
Backup capabilities with RMAN
-
Restore point features with Database Flashback
-
Application continuity in the event of database failover to a standby
For an overview of Oracle’s security and high availability architecture, see the following white papers:
Python Specific Oracle Database resources
Many quick starts, tutorials, and workshops exist specifically for Python developers using Oracle Database. Below are some of the best ones to start with.
Getting Started
If you are looking for a fast way to get started with Python and Oracle Database, check out these two quick start tutorials. These tutorials walk you through installing and setting up the environment you need to connect Python to Oracle Database.
-
Quick Start: Developing Python Applications for Oracle Database
-
Quick Start: Developing Python Applications for Oracle Autonomous Database
Once you have done one of these, then continue with the popular Python and Oracle Database Tutorial: Scripting for the Future to dive deeper to master the Python cx_Oracle interface and see how to build great Oracle Database applications.
Using Different Frameworks with Oracle
-
How to Run SQL Queries with Pandas is a good blog using Pandas for quick and easy data manipulation in Python.
-
Using Oracle with Pandas in OCI Data Science Notebooks dives deeper into using Pandas with large datasets in data science applications.
-
Using SQLAlchemy with Oracle Database provides an excellent toolkit for Python developers using SQLAlchemy as their ORM.
-
Using Django with Python and Oracle Database is a tutorial from Oracle and shows the Django Framework with Python to an Oracle Database.
-
Connecting Pony ORM to the Database is a friendly guide on using Pony with databases.
-
Part 1: Docker for Oracle Database Applications in Node.js and Python.
-
Part 2: Docker for Oracle Database Applications in Node.js and Python.
-
Faster JSON with Python cx_Oracle and Oracle Database 21’s new OSON storage format.
Workshops
The following hands-on, free workshops provide step-by-step instructions and walkthroughs in a live environment.
-
Use Python with Oracle Database 19c is an Oracle LiveLabs workshop that shows how to write Python code to connect to and read data from an Oracle Database, including JSON data.
-
Python and Oracle for Developers is an Oracle LiveLabs workshop that explores the features of the Python cx_Oracle interface for Oracle Database, including efficient techniques for connection management and statement handling.
-
Full Stack Development using Python and deployment via OKE is an Oracle LiveLabs workshop that explores how to build and deploy a simple cloud-native application using the most common frameworks and the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services.
Cloud Development with Oracle Database
The following resources are good starting points for those looking to build applications in the Oracle Cloud and deploy applications in Docker containers and Kubernetes.
-
The Complete Guide To Getting Up And Running With Docker And Kubernetes On The Oracle Cloud.
-
Oracle Cloud Blog has lots of interesting information on different aspects of Oracle Cloud.
For developers looking to focus on application development in the Oracle Cloud and not have to worry about managing the Oracle Database, the Autonomous Database is a good choice. All management, including patching and upgrades, scalability, and security, are entirely autonomous. The following resources offer you a glimpse of its capabilities.
-
Julien Dontcheff’s Database Blog is a good collection of technical posts with the Autonomous Database.
-
SQL Maria also has some excellent posts on all things Oracle Database including Autonomous.
-
An Introduction to Autonomous Database gives you a good overview.
-
Autonomous Database for researchers is a good blog with details on some autonomous features.
General Oracle Database Resources
Here are some Oracle tutorials and resources not specific to Python that can help you take advantage of the Oracle Database features.
-
Oracle Technical Architecture is from Oracle and has nice visuals and short paragraphs on the architecture of the Oracle Database.
-
Oracle Database Internals is an excellent post explaining the architecture of the Oracle Database.
-
This Oracle Performance Tuning blog has a 5-step approach to tuning Oracle.
-
Oracle RAC is another good post on the concepts of RAC, Oracle’s Real Application Cluster software for database high availability.
-
The Oracle Database Security web page has lots of information on Oracle’s solutions for security called “defense in depth.”
-
This is a good post on the Top 5 Reasons to choose Oracle for a production database.
What's next to get your app running?
Full Stack Python
Updates via Twitter & Facebook.